Space Weather Alert - 8th December 2020
What Has Happened?
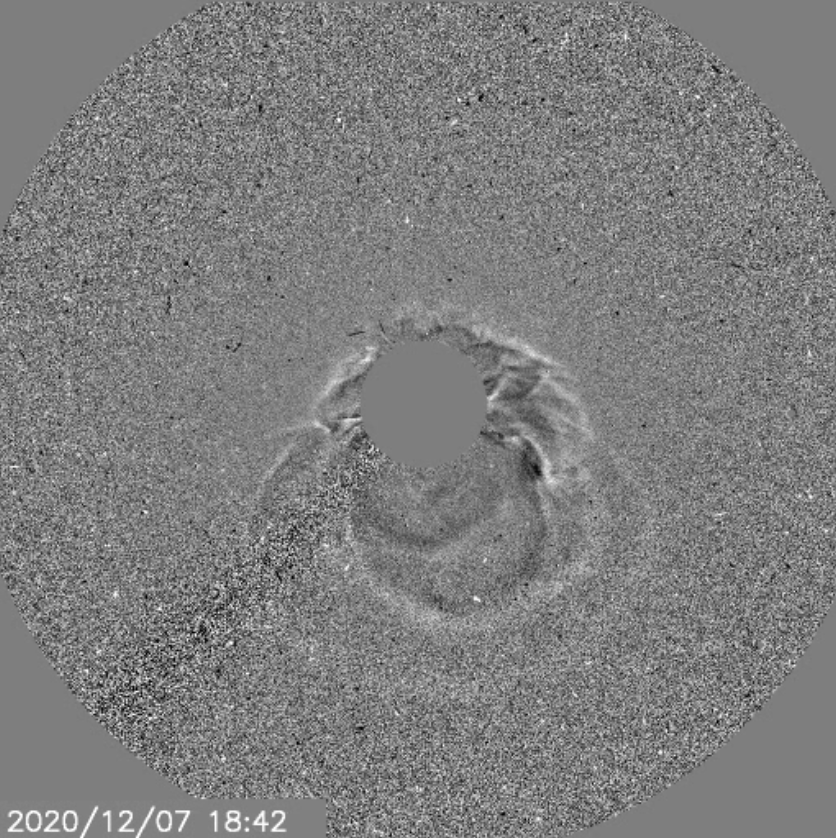
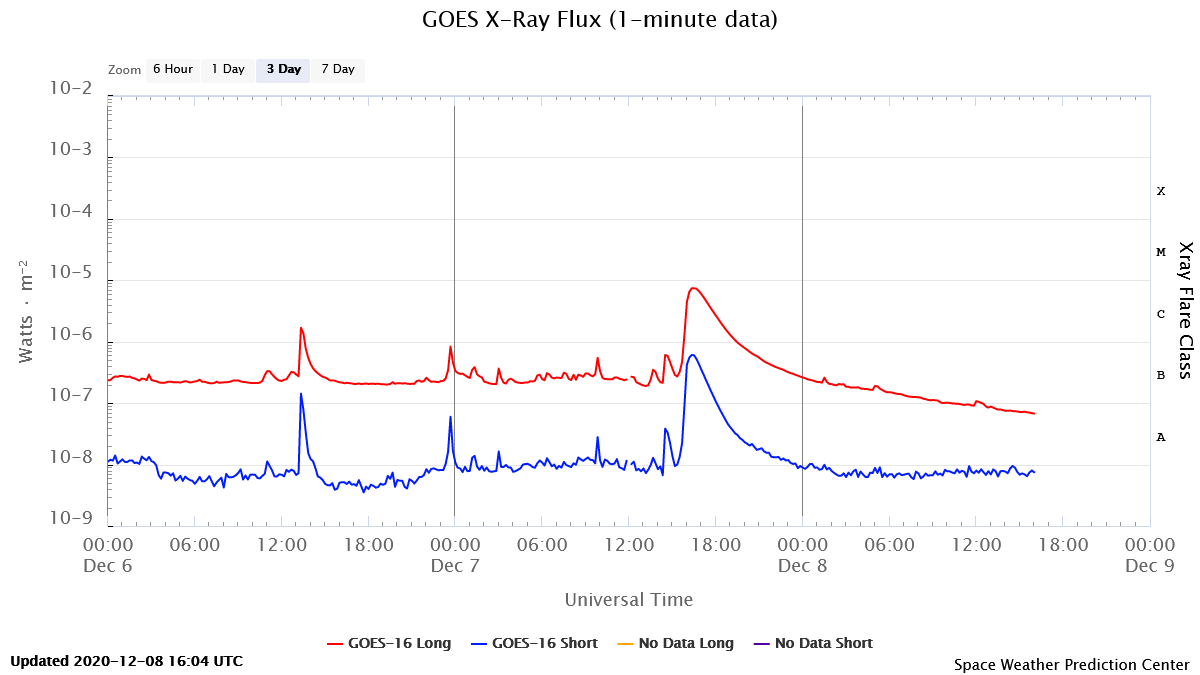
On the 7th December a C7.3 X-ray solar flare erupted from the Sun. This emerged from active region AR12790 which is a small magnetically simple sunspot. Associated with this flare was a coronal mass ejection (CME). This was an asymmetric full-halo event indicating that some of the CME will be Earth-directed. Modelling estimates an arrival late on the 9th December.
In addition, high-speed solar wind from a few small coronal holes is expected to elevate the solar wind speed which may interact with the CME's progress.
In response to the arrival of the CME and high-speed solar wind, geomagnetic activity is expected to become enhanced with activity up to a STORM G1 or even STORM G2 possible. The maximum activity level will depend on the configuration of the solar wind's magnetic field on arrival at Earth.
Assuming clear dark skies, and that the geomagnetic field is suitably disturbed, there is an increased chance of seeing the aurora. In the UK, those in Scotland, northern England and Northern Ireland may have the best opportunities.
Sign-up to receive Geomagnetic Disturbance Alert emails.
Follow us on Twitter:
Follow @BGSauroraAlert for more occasional aurora alerts.
Follow @BGSspaceWeather for daily space weather forecasts.
Glossary
- CME or Coronal Mass Ejection
- The eruption of a portion of the outer atmosphere of the Sun into space, caused by rapid changes in its magnetic field. Often occurs along with a solar flare.
- Coronal Hole
- A region in the Sun’s outer atmosphere (corona) where hot material can flow unrestrained by its magnetic fields out into space.
- Solar Flare
- Energy released by the explosive reorganisation of magnetic fields within the Sun's atmosphere.
- High Speed Stream
- A fast moving stream of solar wind, responsible for magnetic storms.
- Solar Wind
- The ever-present expansion of the Sun’s hot outer atmosphere into the solar system, which carries space weather within it.
- Sunspot/Active Region
- A region of intense magnetic field in the Sun's visible outer atmosphere often associated with flares and CMEs.