Space Weather Alert - 16th February 2023
What Has Happened?
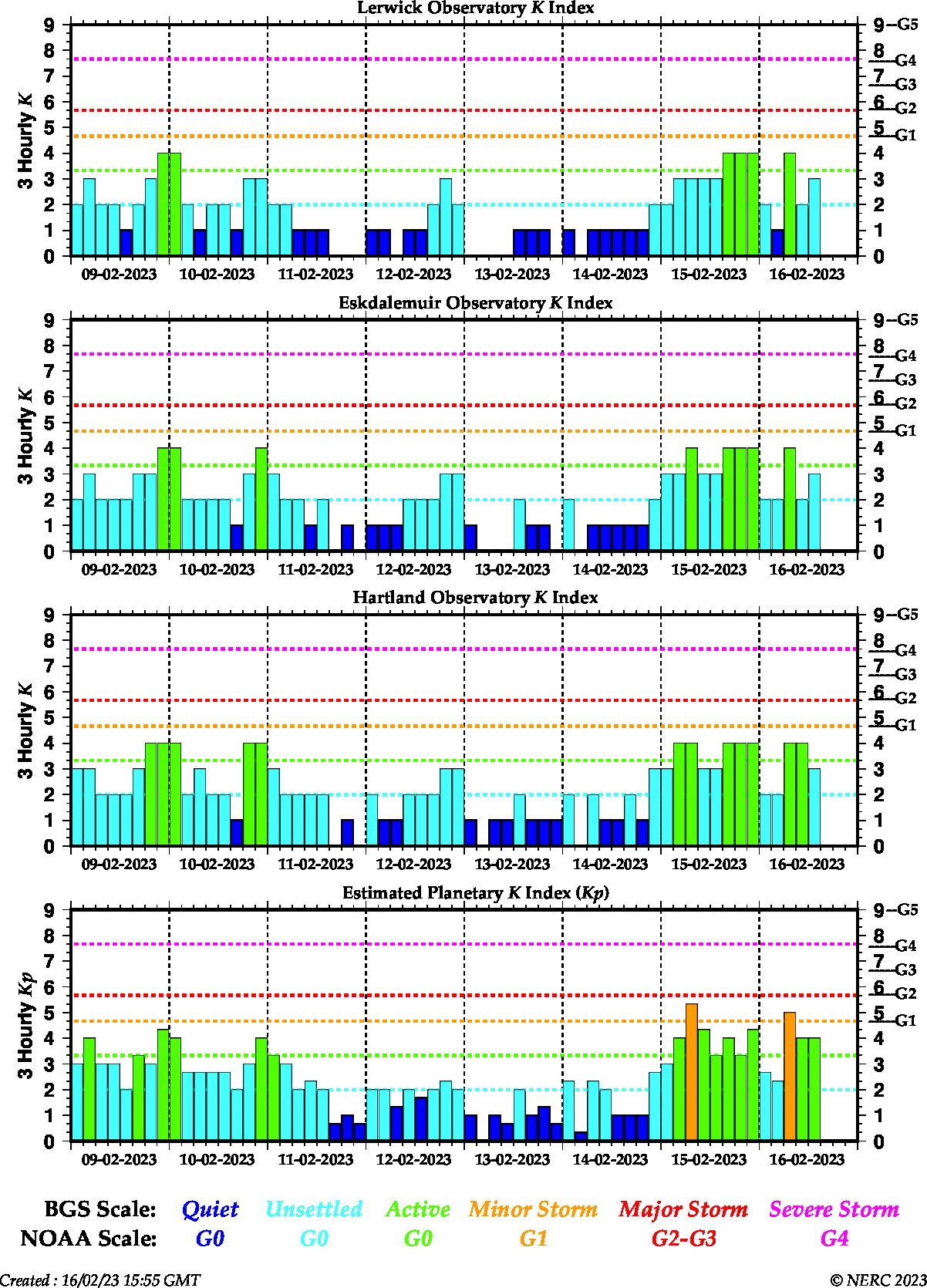
A series of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) have left the Sun during the last week and an increase in geomagnetic activity is expected over the next few days.
Two CMEs from 10th and 11th Feb have already arrived during 13th Feb and 14th Feb, with the latter causing a sustained increase in geomagnetic activity during the 15th Feb reaching STORM levels. In addition, solar wind speed also moderately increased early today (16-Feb), due to coronal hole influence, which have combined with the aforementioned CME effects.
Two further CMEs have been observed; one associated with a filament eruption on 15th Feb, and the other associated with a C-class X-ray solar flare this morning (16th Feb). Given the already increased level of geomagnetic activity, STORM conditions are anticipated following the arrival of these CMEs, the first of which is expected late 17th Feb. Further periods of STORM conditions are possible throughout the upcoming weekend.
Assuming clear dark skies, there is an increased chance of seeing the aurora in the hours following the arrival of the CMEs, particularly at high latitudes in the North of Scotland.
Sign-up to receive Geomagnetic Disturbance Alert emails.
Follow us on Twitter:
Follow @BGSauroraAlert for more occasional aurora alerts.
Follow @BGSspaceWeather for daily space weather forecasts.
Glossary
- BGS
- The British Geological Survey is one of the Natural Environment Research Council's Research Centres.
- CME or Coronal Mass Ejection
- The eruption of a portion of the outer atmosphere of the Sun into space, caused by rapid changes in its magnetic field. Often occurs along with a solar flare.
- Coronal Hole
- A region in the Sun’s outer atmosphere (corona) where hot material can flow unrestrained by its magnetic fields out into space.
- Solar Wind
- The ever-present expansion of the Sun’s hot outer atmosphere into the solar system, which carries space weather within it.
- Solar Flare
- Energy released by the explosive reorganisation of magnetic fields within the Sun's atmosphere.